Multithreading
Multithreading :-
Multithreading in java is a process of executing multiple threads simultaneously. AA thread is a lightweight sub-process, the smallest unit of processing. Multiprocessing and multi threading, both are used to achieve multitasking. However, we use multithreading than multiprocessing because threads use a shared memory area. They don't allocate separate memory area so saves memory, and context-switching between the threads takes less time than process. Java Multithreading is mostly used in games, animation, etc.
Advantages of Java Multithreading:-
1) It doesn't block the user because threads are independent and you can perform multiple operations at the same time.
2) You can perform many operations together, so it saves time.
3) Threads are independent, so it doesn't affect other threads if an exception occurs in a single thread.
Multitasking
Multitasking is a process of executing multiple tasks simultaneously. We use multitasking to utilize the CPU. Multitasking can be achieved in two ways:
- Process-based Multitasking (Multiprocessing)
- Thread-based Multitasking (Multithreading)
1) Process-based Multitasking (Multiprocessing)
- Each process has an address in memory. In other words, each process allocates a separate memory area.
- A process is heavyweight.
- Cost of communication between the process is high.
- Switching from one process to another requires some time for saving and loading registers, memory maps, updating lists, etc.
2) Thread-based Multitasking (Multithreading)
- Threads share the same address space.
- A thread is lightweight.
- Cost of communication between the thread is low.
Thread in java:-
A thread is a lightweight sub process, the smallest unit of processing. It is a separate path of execution.
Threads are independent. If there occurs exception in one thread, it doesn't affect other threads. It uses a shared memory area.
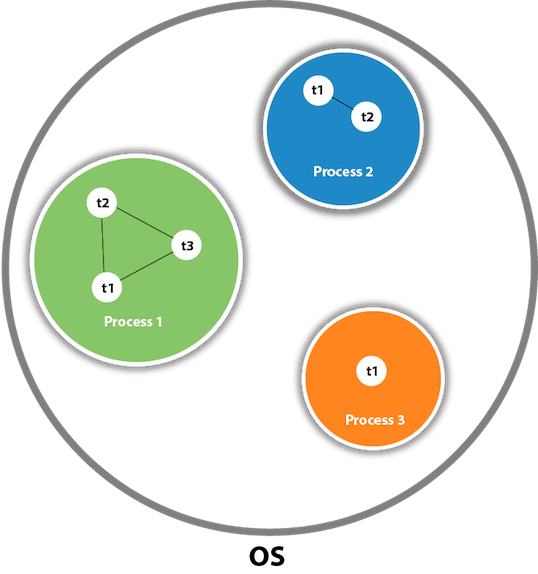
As shown in the above figure, a thread is executed inside the process. There is context-switching between the threads. There can be multiple processes inside the OS, and one process can have multiple threads
Java Thread class
Java provides Thread class to achieve thread programming. Thread class provides constructors and methods to create and perform operations on a thread. Thread class extends Object class and implements Runnable interface.
Java Thread Methods:-
|
S.N. |
Modifier
and Type |
Method |
Description |
|
1) |
void |
It is used to start the execution of the thread. |
|
|
2) |
void |
It is used to do an action for a thread. |
|
|
3) |
static void |
It sleeps a thread for the specified amount of time. |
|
|
4) |
static Thread |
It returns a reference to the currently executing
thread object. |
|
|
5) |
void |
It waits for a thread to die. |
|
|
6) |
int |
It returns the priority of the thread. |
|
|
7) |
void |
It changes the priority of the thread. |
|
|
8) |
String |
It returns the name of the thread. |
|
|
9) |
void |
It changes the name of the thread. |
|
|
10) |
long |
It returns the id of the thread. |
|
|
11) |
boolean |
It tests if the thread is alive. |
|
|
12) |
static void |
It causes the currently executing thread object to
pause and allow other threads to execute temporarily. |
|
|
13) |
void |
It is used to suspend the thread. |
|
|
14) |
void |
It is used to resume the suspended thread. |
|
|
15) |
void |
It is used to stop the thread. |
|
|
16) |
void |
It is used to destroy the thread group and all of its
subgroups. |
|
|
17) |
boolean |
It tests if the thread is a daemon thread. |
|
|
18) |
void |
It marks the thread as daemon or user thread. |
|
|
19) |
void |
It interrupts the thread. |
|
|
20) |
boolean |
It tests whether the thread has been interrupted. |
|
|
21) |
static boolean |
It tests whether the current thread has been
interrupted. |
|
|
22) |
static int |
It returns the number of active threads in the current
thread's thread group. |
|
|
23) |
void |
It determines if the currently running thread has
permission to modify the thread. |
|
|
24) |
static boolean |
It returns true if and only if the current thread holds
the monitor lock on the specified object. |
|
|
25) |
static void |
It is used to print a stack trace of the current thread
to the standard error stream. |
|
|
26) |
StackTraceElement[] |
It returns an array of stack trace elements
representing the stack dump of the thread. |
|
|
27) |
static int |
It is used to copy every active thread's thread group
and its subgroup into the specified array. |
|
|
28) |
Thread.State |
It is used to return the state of the thread. |
|
|
29) |
ThreadGroup |
It is used to return the thread group to which this
thread belongs |
|
|
30) |
String |
It is used to return a string representation of this
thread, including the thread's name, priority, and thread group. |
|
|
31) |
void |
It is used to give the notification for only one thread
which is waiting for a particular object. |
|
|
32) |
void |
It is used to give the notification to all waiting
threads of a particular object. |
|
|
33) |
void |
It sets the context ClassLoader for the Thread. |
|
|
34) |
ClassLoader |
It returns the context ClassLoader for the thread. |
|
|
35) |
static Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler |
It returns the default handler invoked when a thread
abruptly terminates due to an uncaught exception. |
|
|
36) |
static void |
It sets the default handler invoked when a thread
abruptly terminates due to an uncaught exception. |

Comments
Post a Comment